Modern construction is changing quickly. Steel building construction is now one of the most reliable and efficient solutions for global infrastructure. Steel is strong, fast, and adaptable. Because of this, it is now important in industrial, commercial, agricultural, and residential projects.
This guide explains how steel building construction works. It covers important parts, customization options, and how steel compares to traditional materials.
1. What Is Steel Building Construction?
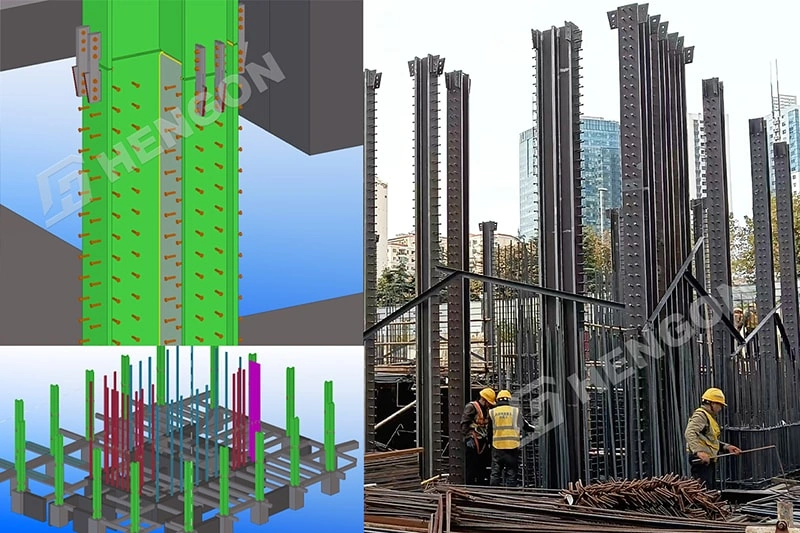
Steel building construction refers to the design, fabrication, and erection of structures made primarily from steel components. These buildings use strong steel frames, smart connections, and modern panels. This makes them durable, affordable, and easy to put together.
Steel work in construction offers several core advantages:
Higher load-bearing capacity
Faster construction timelines
Long service life with minimal maintenance
Excellent seismic, wind, and fire resistance
Full customization for different uses
Steel structure construction is now widely used in warehouses, workshops, factories, schools, cold storage buildings, residential houses, and more.
2. Common Types of Steel Structure Buildings
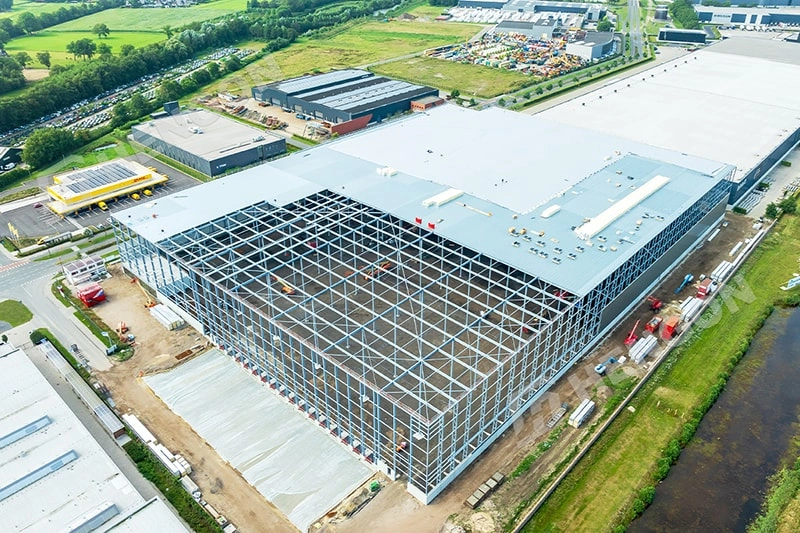

Pre-Engineered Metal Building (PEB)
PEB systems are made in controlled factory conditions. This ensures quick assembly on-site and lowers project costs.
Two-Story Steel Buildings
Ideal for office-plus-warehouse setups, commercial facilities, or residential conversions.
Single-Slope Steel Buildings
Popular for workshops, farm buildings, and logistics centers requiring efficient drainage and simplified design.
Steel Arch Houses / Arch Buildings
A unique curved structure used for storage, livestock, and residential applications.
I-Shaped Metal Buildings
Using I-beam steel for superior load capacity in industrial settings.
Gambrel Metal Buildings
Barn-style structures with additional headroom, perfect for agriculture or commercial use.
3. Key Components in Steel Work for Construction
Understanding the building’s core elements is essential for successful steel structure construction. Major components include:
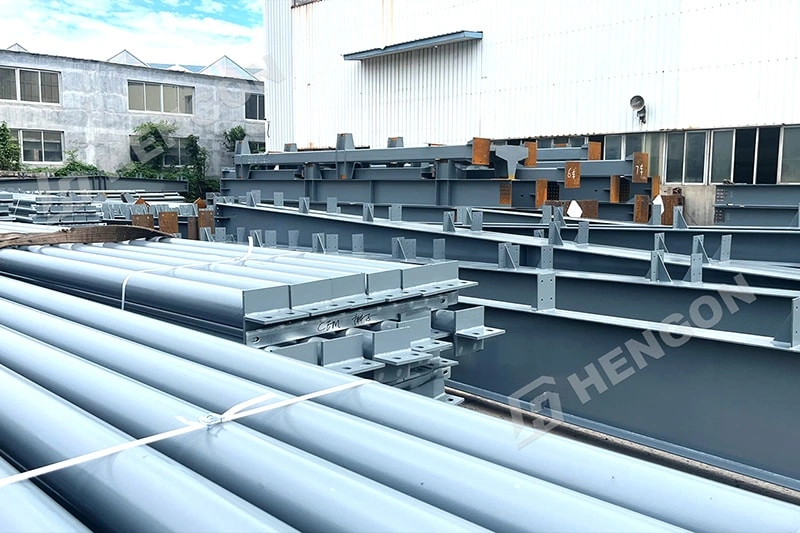

Foundations & Metal Building Footings
Steel buildings typically use concrete slab foundations, pier footings, or a combination of both. Proper foundation design ensures long-term stability.
Columns, Beams & Frame System
Q355 or equivalent high-strength steel is commonly used for primary framing.
Roof & Wall Panels
Options include:
Rock wool panels (fireproof)
EPS or PU sandwich panels
Corrugated metal sheets
ALC panels (for high insulation requirements)
Windows for Metal Buildings
PVC, aluminum, or steel windows can be added depending on insulation and aesthetic needs.
Essential Metal Building Details
Trim, flashing, gutters, downpipes, and fasteners ensure durability and weather protection.
4.The Steel Building Construction Process
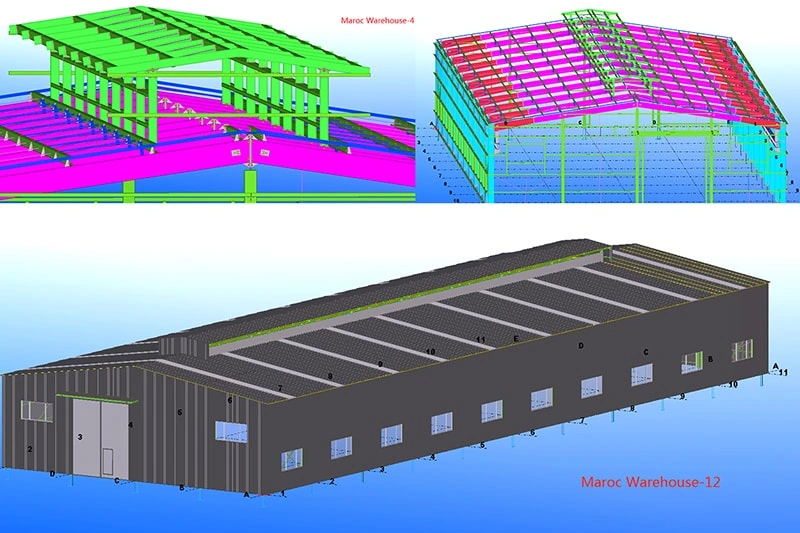
Step 1: Design & Engineering
Structural engineers determine loads, dimensions, and steel grades. BIM and 3D modeling ensure accuracy.
Step 2: Fabrication
All beams, columns, bracing, and panel systems are manufactured off-site under strict quality control.
Step 3: Delivery & On-Site Erection
Because components arrive pre-fabricated, metal building erection is fast and efficient.
Bolted connections, crane lifting, and panel installation ensure quick completion.
Step 4: Finishing & Inspection
Doors, windows, insulation, interior partition walls, and electrical systems are installed.
5. Customization & Expansion Options
Steel structures are highly adaptable and can evolve with project needs. Popular options include:
Adding a Lean-To to a Metal Building
Perfect for extensions, loading areas, garages, or shaded spaces.
Steel Building With Porch
Adds both functionality and architectural appeal.
Color Customization (e.g., Charcoal Grey Metal Building)
Brands often choose color systems that match identity and climate needs.
Special Layouts (e.g., 15,000 sq ft Metal Building)
Large-scale facilities for manufacturing, logistics, and agriculture.
I-Shaped, Gambrel, and Modern Residential Steel Designs
Architectural flexibility makes steel suitable for living spaces as well.
6. Living or Working in a Steel Building
Steel buildings are no longer limited to industrial use—many serve as residences, offices, or mixed-use facilities.
Insulating a Metal Building After It Is Built
Common insulation methods include:
Rock wool
Glass wool
PU/PIR panels
Spray foam
Proper insulation reduces energy consumption and improves comfort.
Interior Space Planning
Steel frames allow large clear-span interiors, making layout changes easy at any stage.
Comfort, durability & safety
Steel buildings resist moisture, termites, rot, and fire—making them ideal for long-term occupancy.
7. Maintenance and Long-Term Durability
Steel structures have impressive longevity due to:
Minimal maintenance requirements
Advanced coatings for corrosion resistance
Superior load-bearing stability
Flexible design adaptations
Periodic checks of bolts, gutters, and coatings help extend the building’s lifespan.
8. Popular Applications of Modern Steel Buildings
Steel building construction is used in:
Warehouses & logistics centers
Workshops & metal fabrication shops
Commercial showrooms
Agricultural barns & chicken houses
Prefabricated homes & villas
Energy or mining facilities
Storage & distribution centers
[See our project portfolio here]
9. Conclusion: Why Steel Building Construction Leads the Future

Steel structures offer unmatched speed, efficiency, strength, and flexibility—far beyond what traditional construction methods can deliver. As industries demand sustainable and cost-effective solutions, steel building construction continues to expand across all sectors.
No matter if you are planning a new warehouse, workshop, steel home, or industrial building, steel is the best choice for modern construction.