1. Introduction
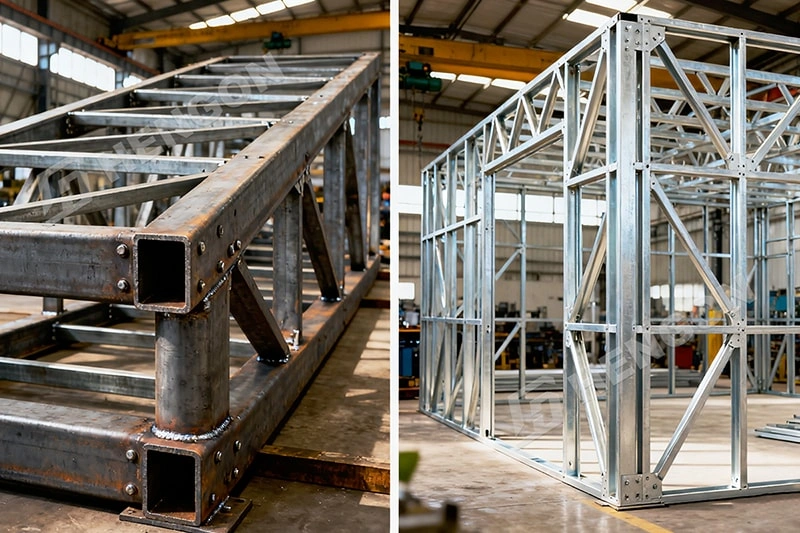

Structural steel and light gauge steel are two of the most widely used materials in modern construction. While they may appear similar, their production methods, applications, fastening systems, and performance characteristics differ significantly.
Understanding these differences is essential for architects, engineers, and developers when choosing the right material for any project.
2. What Is Structural Steel?
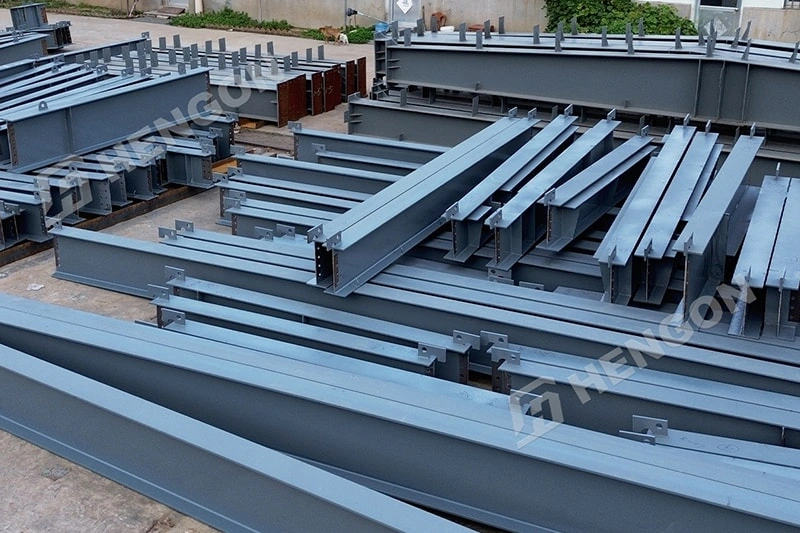

Structural steel refers to hot-rolled, heavy-duty steel sections used to form the primary skeleton of large structures.
These components provide exceptional strength and are commonly used in:
Warehouses and industrial workshops
Large-span buildings
High-rise structures
Bridges
Heavy-load platforms
Common types of structural steel used in construction include:
Universal Beams (UB)
Universal Columns (UC)
Tapered Flange Beams
Rectangular / Square Hollow Sections
Parallel Flange Channels
Tubular Hollow Sections
Structural steel is known for its high load-bearing capacity, long-term durability, and excellent performance in demanding environments.
3. What Is Light Gauge Steel?
Light gauge steel—also called cold-formed or cold-rolled steel—is manufactured by bending thin steel sheets into shape at room temperature.
This production method increases precision, reduces weight, and allows efficient prefabrication.
Light gauge steel is commonly used for:
Residential buildings
Apartment units
Commercial interior partitions
Modular structures
Light commercial projects
It does not rot, warp, or attract pests, and is significantly lighter than structural steel and concrete.
4. Differences in Production Methods
Hot-rolled
Thick, heavy sections
Designed for high load-bearing structures
Light Gauge Steel
Cold-formed
Thin, precise sections
Ideal for prefabricated, lightweight applications
These manufacturing differences directly affect performance, installation, and project suitability.
5. Fastening & Installation Differences
Structural Steel typically requires:
Welding
Bolting
Riveting
These heavy fastening methods ensure stability in large and complex structures.
Light Gauge Steel uses:
Steel screws
Clip connections
Lightweight tools
This makes installation faster, cleaner, and more flexible, especially for tight construction schedules.
6. Advantages of Light Gauge Steel
Light gauge steel is widely appreciated for benefits such as:
Faster construction time
Reduced material weight
Eco-friendly with recyclable materials
Lower labor requirements
Cleaner and safer job sites
Highly customizable and precise fabrication
Can be constructed during winter
Lower overall installation cost
High resistance to moisture, pests, corrosion, and rot
Excellent fire ratings
These advantages make it an attractive choice for residential and modular construction.
7. Advantages of Structural Steel
Structural steel offers strong advantages for heavy-duty projects:
Exceptional load-bearing capacity
Superior strength for long spans
Highly durable in industrial environments
Suitable for multi-storey and large-scale buildings
Excellent seismic and wind resistance
Long service life with minimal maintenance
8. Applications in the Construction Sector
Structural Steel Applications
Industrial plants and workshops
Warehouses
Multi-floor buildings
Heavy-load bridges
High-wind or seismic zones
Light Gauge Steel Applications
Residential houses
Apartment buildings
Offices and commercial interiors
Prefabricated modular units
Temporary or relocatable structures
9. How to Choose Between the Two
The right type of steel depends on:
Building load requirements
Span and building height
Budget and construction timeline
Environmental conditions
Fire and safety requirements
Local building standards
Prefabrication needs
Projects requiring heavy loads, large spans, or high structural strength should choose structural steel.
Projects needing fast installation, lighter materials, and modular or residential solutions may benefit more from light gauge steel.
10. Conclusion

Both structural steel and light gauge steel play critical roles in modern construction.
While structural steel excels in strength and durability, light gauge steel offers precision, speed, and lightweight efficiency.
The best choice depends on your project’s unique requirements, objectives, and long-term performance expectations.